About Cracks in Foundation Walls
Foundation Cracks in poured concrete walls can be found in almost all residential foundations. Most often, they occur in corners, from corners of windows, pour lines, holes for service lines or rod ties.
- The various causes include:
- improper concrete mix (high water content),
- rapid concrete curing,
- improper expansion control joints,
- premature removal of concrete forms (2 days instead of 7),
- compressible soil,
- premature backfilling,
- improper compaction of fill soil,
- expansive clay soils,
- uneven moisture around the foundation,
- plumbing leaks,
- poor drainage,
- hydrostatic water pressure.
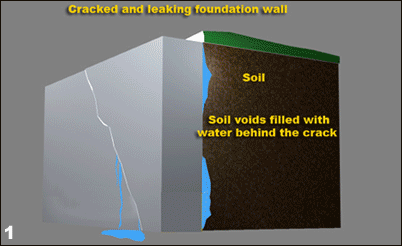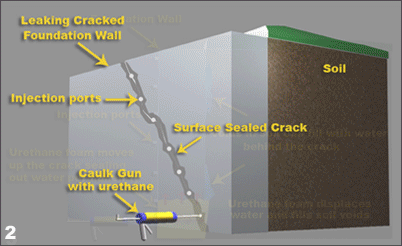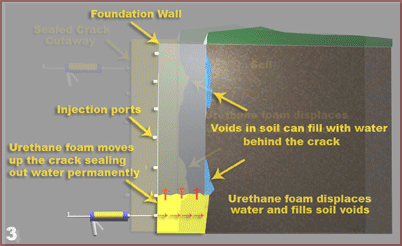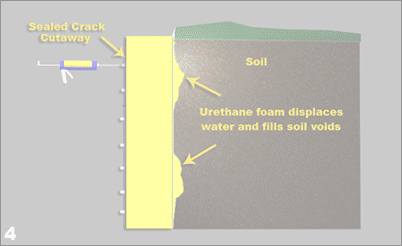
All houses settle. Because of variations in soil properties, not every point on a foundation settles uniformly, which may cause racking doorframes and cracking walls. Good construction prevents differential settlement and minimizes the overall settlement.
Over time, even minor cracks can grow larger and cause big headaches, such as loss of structural integrity. Repair all cracks exposed to moisture as quickly as possible to avoid more extensive damage.
Types of Basement Wall Cracks
Shrinkage Cracks
Hairline cracks typically develop within the first month and most foundations cracks appear within the first year. In most cases, the common wall cracks pose no structural concerns of foundation failure. The biggest problem they cause is water leakage.

Settlement Cracks
In a poured concrete foundation wall, the typical foundation crack will run vertically or at an angle. It is caused by shrinkage of the concrete as it cures. Settlement cracks are also nearly always vertical. Such non-structural foundation cracks can be easily repaired by polyurethane foam injection.

Structural Cracks
Clay soils in some areas are highly expansive. As the soil gets repeatedly wet and dry, it expands and shrinks, exerting lateral pressure on the foundation walls. If you have horizontal cracks along the midpoint of the wall, the wall is subjected to lateral pressure, which could bow and structurally damage the wall.

About Cracks in Foundation Walls
Cracks more than 1/4-inch wide, horizontal cracks in walls, cracks with misaligned edges or continuing movement may require professional assessment. You can monitor the crack’s length and movement by marking off the ends of the crack and making several “alignment marks” across the crack at various points.
Ottawa Foundation repair contractors can fix failed foundations:
· Slab jacking involves pumping a cement grout through small holes in the concrete slab
· Piering involves strategically placed mechanical jacks for lifting the settled beam to grade.
· Injection is the Best Repair of Poured Concrete Walls
Crack injection works by filling the full length and depth of the crack with expandable polyurethane foam or epoxy. It is permanent – the repair does not have to be repeated. Unlike any surface repair, the injected polymer is not vulnerable to weathering, ultraviolet rays or traffic.
Filling the full depth of the crack rather than just bridging it prevents further deterioration of the concrete by groundwater. In addition, the injected polymer coats reinforcing steel and starves the corrosion process.
But most importantly, crack injection prevents future expensive problems. The potential damages done by water leaks to the finished basement or the cost of repairing concrete spalls caused by corrosion of reinforcing steel make clear the advantages of permanent crack repair.
